Osazone Test Definition
Osazone test is a chemical test used to detect reducing sugars. This test even allows the differentiation of different reducing sugars on the basis of the time of appearance of the complex. This test is also termed Phenyl hydrazine test based on the reagent used for this test.
Objectives of Osazone Test
- To detect reducing sugars.
- To differentiate reducing sugars from non-reducing sugars.
- To distinguish different reducing sugars between each other.
Principle of Osazone Test
- The reagent for this test consists of phenylhydrazine in acetate buffer.
- This test is based on the fact that carbohydrates with free or potentially free carbonyl groups react with phenylhydrazine to form osazone.
- The condensation-oxidation-condensation reaction between three molecules of phenylhydrazine and carbon one and two of aldoses and ketoses yields 1, 2-diphenyhydrazone, which is known as osazone.
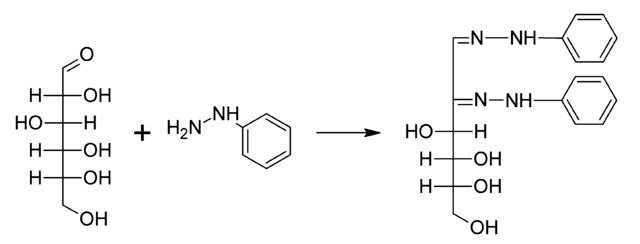
Figure: A typical reaction showing the formation of an osazone. D-glucose reacts with phenylhydrazine to give glucosazone.
- Osazone appears as yellow-colored crystals of characteristic shape, solubility, melting point, and time of formation. Osazone is different for different sugars.
- Since both carbons 1 and 2 are involved in the reaction, C-2 epimers produce the same osazone.
- Similarly, ketoses with a configuration identical to aldoses below C-2 give the same osazones, e.g. glucose and fructose.
Requirements
Reagent
- Osazone mixture: 0.5 g of phenylhydrazine hydrochloride and 0.1 g of sodium acetate.
- Glacial acetic acid
- Test sample
Materials required
- Test tubes
- Test tube stand
- Pipettes
Equipment
- Vortex
- Water bath
- Microscope
Procedure of Osazone Test
- Take 5 ml of test solution in a clean, dry test tube.
- Add 0.3 g of osazone mixture and five drops of glacial acetic acid to the test tube.
- Mix it well and warm the test tube gently in the water bath if required to dissolve all the elements.
- Keep the test tube in boiling water and observe the formation of crystals at various time points.
- Observe the shape of the crystal under low magnification under a microscope.
Result and Interpretation of Osazone Test
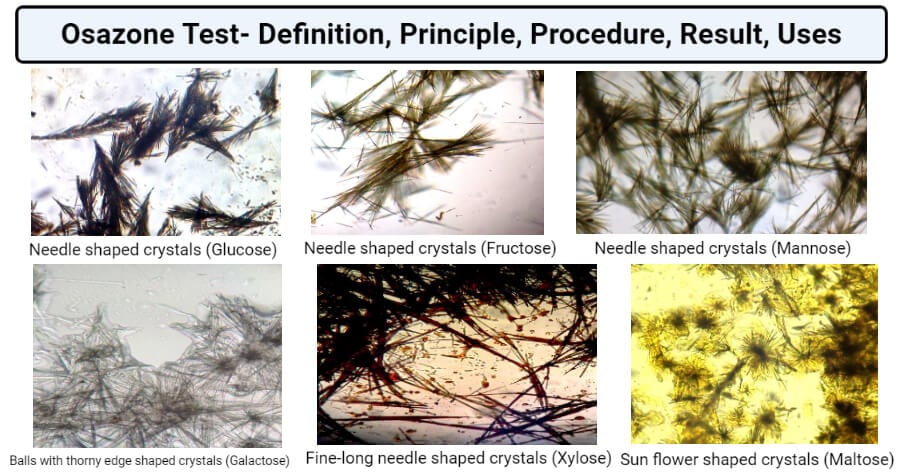
- Based on the shape and structure of the crystals and their time of appearance, different sugars can be identified.
- The following is a chart for the identification of reducing sugar through this test:
| Carbohydrate | Time of formation (min) | Crystalline structure |
| Fructose | 2 | Needle shape |
| Glucose | 5 | Needle shape |
| Galactose | 20 | Thorny ball shape |
| Maltose | 30-45 | Sunflower/ star shape |
| Lactose | 30-45 | Cotton ball/ powder puff shape |
- Thus, through this table, different sugars can be identified on the basis of the structure of the crystal and the time of appearance.
Uses of Osazone Test
- This test is the only test that can be used to distinguish lactose from maltose during the identification of unknown sugars.
- This is a simple, cheap, and relatively less time-consuming test for the identification and differentiation of different sugars encountered in clinical practice.
- This test can also be used for locating sugars in plant tissues.
Limitations of Osazone Test
- This test gives a positive result for sucrose when if boiled for 30 minutes or more even though sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
- This test is not effective if the sample contains a mixture of different sugars.
- Similarly, large quantities of sugars are required for a positive result.









0 Comments