SGPT (ALT, Alanine aminotransferase, Serum Glutamic-Pyruvic Transaminase)
Sample
- This is done on the serum of the patient.
- The Blood sample can be taken at any time.
- The fasting sample is not necessary.
- Analyze the enzyme on the same day because the enzyme activity is lost at room temperature.
- This enzyme is stable in whole blood up to 12 to 24 hours; after that time, there is a gradual increase due to release from the RBCs.
- The sample can be stored at 4 °C for 1 to 3 days (ALT is stable when refrigerated).
- ALT, when freezed, shows deterioration.
Precautions
- Avoid hemolysis because RBC contains increased ALT (SGPT) and AST (SGOT).
- Drugs that may increase the SGPT value are acetaminophen, aminosalicylic acid, ampicillin, allopurinol, cephalosporin, chlorpropamide, clofibrate, cloxacillin, codeine, indomethacin, INH, Methyldopa, methotrexate, nalidixic acid, quinidine, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, salicylates, tetracycline, and propanol.
- Ideally, perform the test as soon as possible or on the same day because the sample’s storage may not be satisfactory.
- Previous I/M injection may increase the level.
Indications
- Diagnose liver diseases.
- Monitor liver diseases after the treatment.
- It differentiates jaundice from liver disease or hemolytic anemia.
Pathophysiology
- Definition of ALT (SGPT):
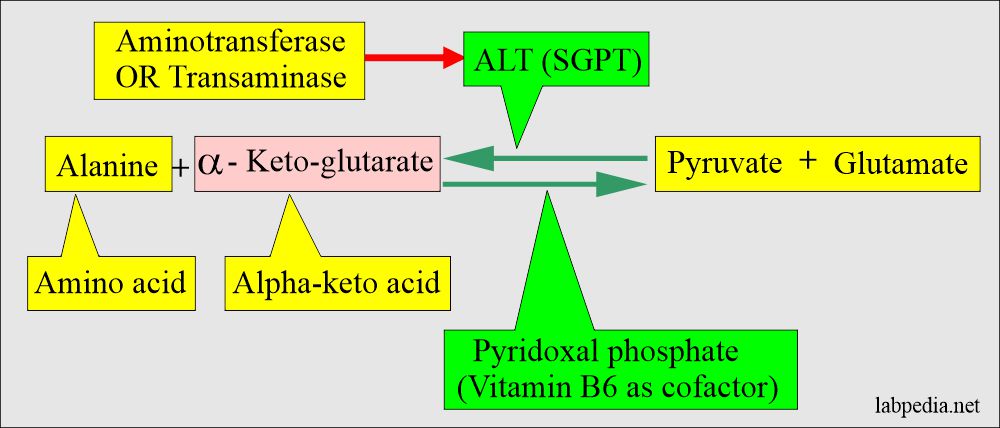
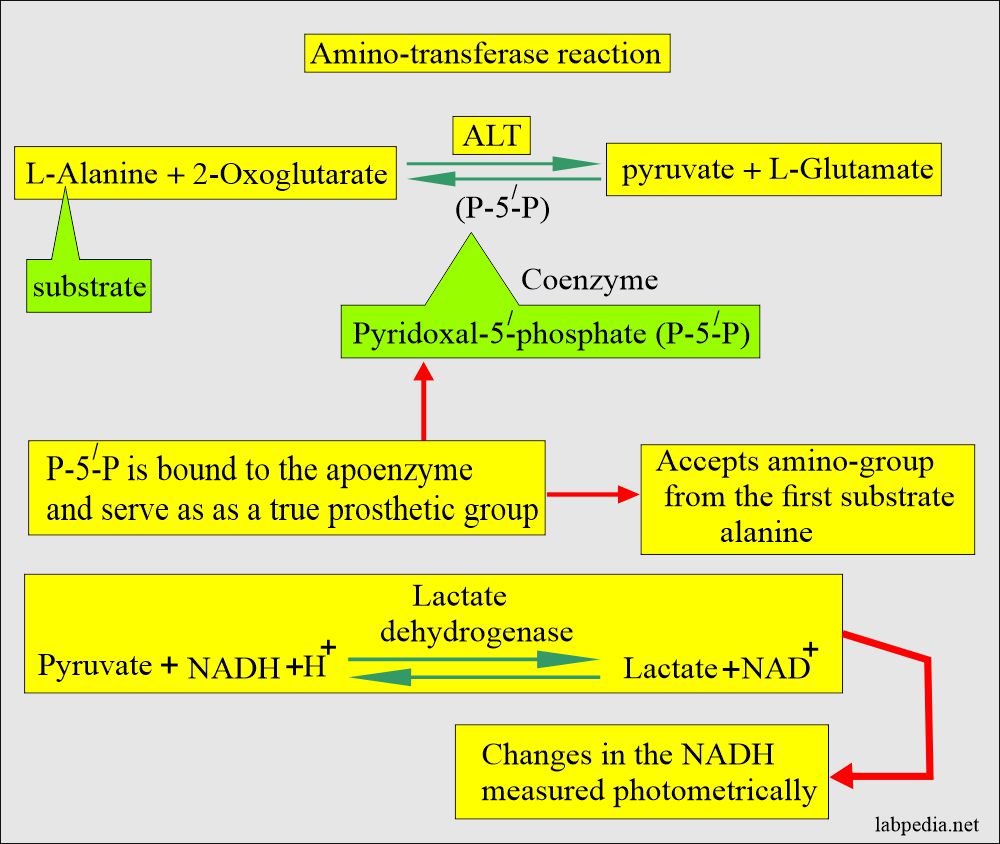
- This enzyme catalyzes the reversible transfer of amino groups between an amino acid, and α-keto acids are called aminotransferase or transaminases.
- One of the aminotransferases is Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), or the old name was glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (SGPT) which will catalyze the reversible transfer of the amino group between an amino acid and α-keto acid where vitamin B6 (pyridoxal phosphate) is the co-factor.
- Distribution of SGPT (ALT):
- ALT is an enzyme found predominantly in the liver.
- It is distributed in many tissues, a moderate amount in:
- Kidneys.
- A small amount in:
- Heart, skeletal muscles.
- A minimal amount may be found in the pancreas, spleen, lungs, and RBCs.
- Variation of the ALT:
- The day-to-day variation of the ALT is 10% to 30%, and there is diurnal variation.
- ALT is 45% higher in the afternoon than in the early morning.
- Until the age of 15, ALT is higher than the AST; after that, AST is higher than the ALT.
- In few people, this pattern may reverse after the age of 60.
- Exercise is the major determinant for AST and but less for ALT in men.
- Strenuous exercise or bodybuilding increase 3 fold AST and 50% increase in ALT.
- The effect of the exercise is minimal in the women.
- Distribution of SGPT (ALT) in the liver:
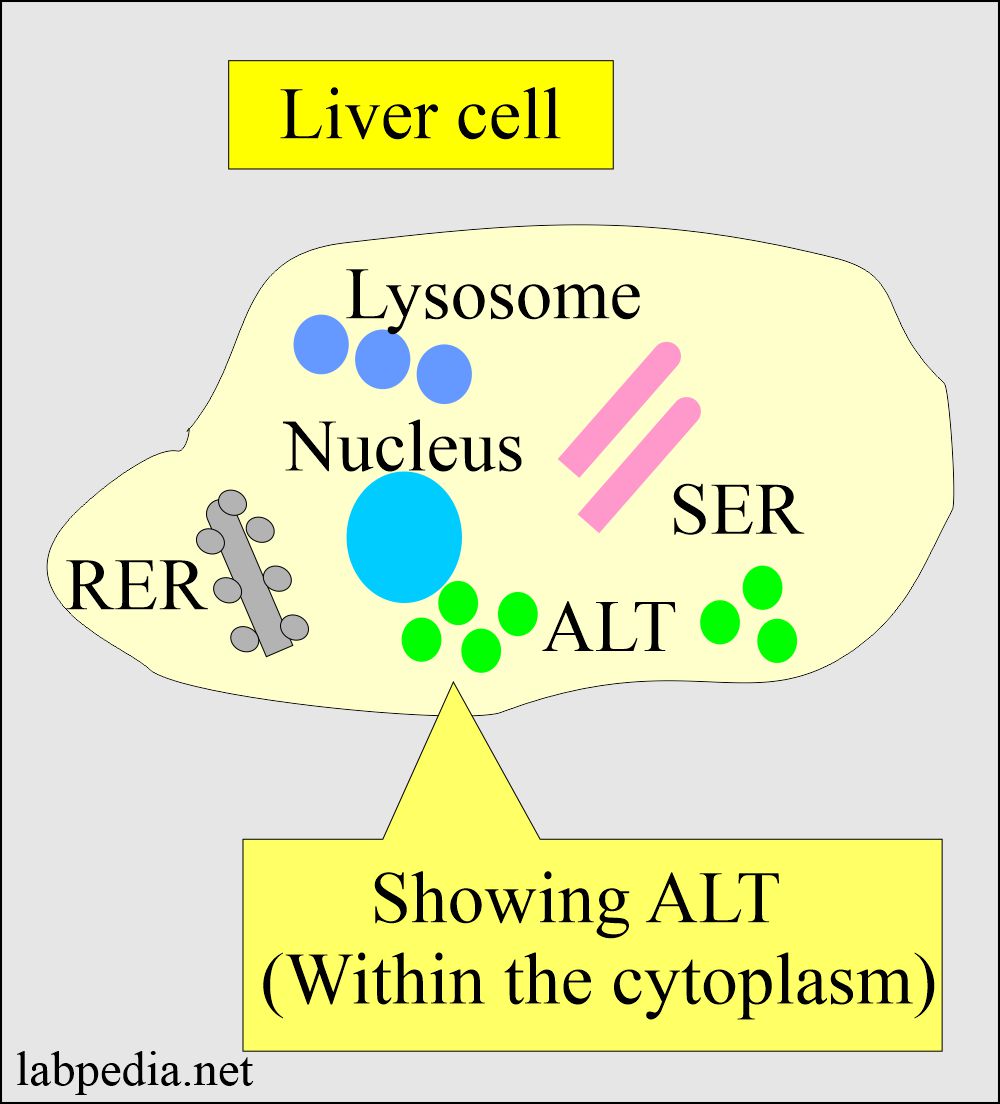
- This enzyme is present in cytosolic and mitochondrial forms in the liver. The majority of the SGPT is present in the cytoplasm of liver cells.
- There is always a low level of this enzyme in the blood.
- This is a liver-specific enzyme of the transferases.
- The liver hepatocytes contain 3 to 4 times more AST (SGOT) than the ALT (SGPT).
- This is also normally found in bile, CSF, and saliva.
- It is not found in the urine unless there is a kidney lesion.
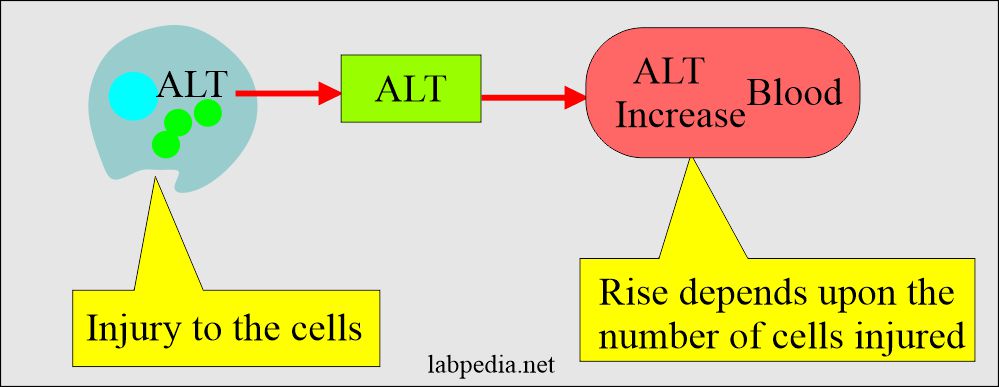
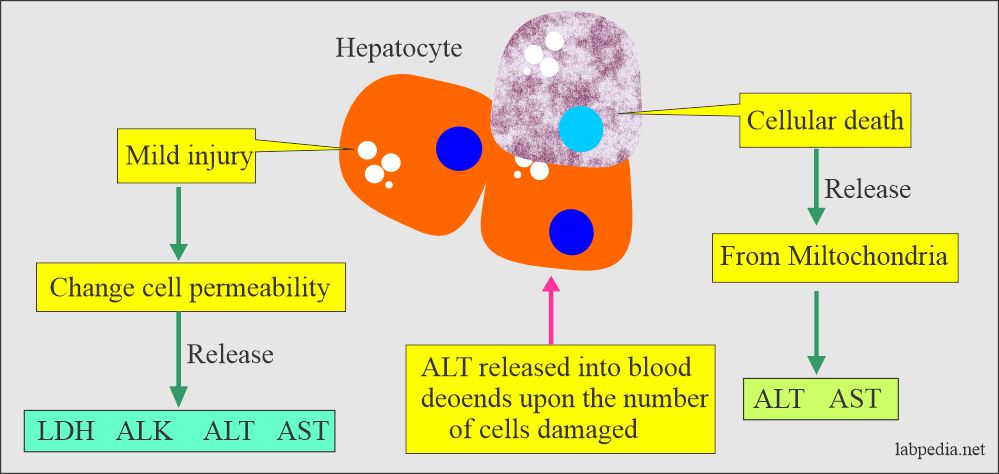
- Liver cell injury: Any damage to the liver cells, SGPT enzyme, is released, specifically for liver cell necrosis.
- First cytosolic SGPT is released, and in the case of necrosis, then mitochondria SGPT is released into circulation.
- SGPT activity persists longer than the SGOT.
- This enzyme is raised before there are clinical findings of jaundice.
- In viral hepatitis, the SGPT/SGOT ratio is greater than 1.
- Other than the viral cause, the SGPT/SGOT ratio is less than 1.
SGPT (ALT) biochemical reaction and variations in different conditions:
- ALT catalyzes the reaction, and it is reversible.
- Pyridoxal-5‘- phosphate (P-5-P) functions as coenzymes in the amino-transfer reaction.
- The P-5-P is bound to the apoenzyme and serves as a true prosthetic group.
- The P-5-P bound to the apoenzyme accepts the amino group from the first substrate, alanine, to form enzyme-bound pyridoxine-5- phosphate, and the first reaction product is pyruvate.
- This coenzyme increases the ALT activity by 20% in the normal serum.
- Hemolysis increases both AST and ALT because of this enzyme activity in the RBCs in comparison to serum. This effect is greater for AST than ALT.
- SGPT 1.5 to 8 times more than the normal level seen in:
- Early, late and subclinical hepatitis.
- Chronic hepatitis.
- Alcoholic hepatitis.
- Chemical hepatitis.
- Passive congestion with centrilobular necrosis.
- Rye’s syndrome.
- Cholangitis.
- Hemochromatosis.
- SGPT >8 to 10 times more than the normal value seen in:
- Mostly in acute viral hepatitis.
- SGPT >30 times more than the normal value is seen in:
- Drug toxicity like acetaminophen in alcoholics and malnourished people.
| Organs | Times more as compared to the serum normal level |
| Liver | 2850 |
| Kidneys | 1200 |
| Heart | 450 |
| Skeletal muscle | 300 |
| Pancreas | 130 |
| Spleen | 80 |
| Lungs | 45 |
| RBCs | 7 |
| Serum | 1 |
AST/ALT ratio:
- The ALT is the cytoplasmic enzyme in the liver, while AST is both cytoplasmic and mitochondrial enzyme with a wide distribution in the various other tissues.
- AST/ALT ratio normally is <1, but in the liver, infectious hepatitis becomes greater.
- AST/ALT ratio is usually greater than 1 in:
- The patient with alcoholic liver diseases (cirrhosis). AST is more sensitive to alcoholic liver disease.
- Liver congestion.
- Metastatic tumor of the liver.
- AST/ALT ratio of less than 1 is seen in:
- Acute hepatitis.
- Viral hepatitis.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- The ratio will be less accurate if the AST level is more than 10 times the normal.
Ratio of enzymes <1 >1 AST/ALT - Acute hepatitis
- Viral hepatitis with extensive hepatocellular necrosis
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Alcoholic liver diseases (Cirrhosis)
- Alcoholic patient with acetaminophen, causing extensive liver cell necrosis.
- Liver congestion
- Metastatic tumor infiltration of the liver
- Myocardial infarction
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Hemolytic anemia
- Diagnostic application of the SGPT (ALT):
- The best indicator for liver cell injury when both SGPT and SGOT are raised.
- Higher-level are found in hepatocellular disorders than the extrahepatic or intrahepatic obstructive lesions.
- Levels of both enzymes may reach as high as 100 times. 20 to 50 times, the elevated level is frequently found.
- Measuring aminotransferases weekly is useful in hepatitis or other hepatic injuries.
- Because of the accurate measuring techniques, it can detect liver cell injury due to alcohol.
- It is used as a screening test for diagnosing hepatitis due to hepatotropic viruses, especially the hepatitis C virus in blood donors.
- 5 to 10 times the elevation of both ALT and AST occurs in the liver’s metastatic carcinoma. AST (SGOT) level is higher than the ALT (SGPT). In the early stages of malignant infiltration of the liver, these enzymes are normal.
- ALT (SGPT) may be raised after intake of alcohol, delirium tremors, and after the administration of the drugs like opiates, salicylates, and ampicillin.
NORMAL
Source 4
| Age | Male U/L | Female U/L |
| Newborn 12 months | 13 to 45 | 13 to 45 |
| one to 60 years | 10 to 40 | 7 to 35 |
| 60 to 90 years | 13 to 40 | 10 to 28 |
| >90 years | 6 to 38 | 5 to 24 |
Source 2
- Adult / child = 4 to 36 unit/L at 37 °C
- Elderly = slightly higher than the adult
- Infants = Maybe twice high as the adult
Another source
- Men = 10 to 30 units /L (some labs normal is 10 to 40 U/L).
- Women = 9 to 25 units /L (Some labs normal is 10 to 28 U/L).
- Children two times of adult’s value.
- In children, it is raised because of bone activity, and that is normal for children.
- The adult level is achieved by 6 months of age.
- Males are slightly higher than females.
The Increased SGPT (ALT) Level Is Seen In:
- Viral hepatitis. There is markedly increased the level.
- Drug-induced hepatitis.
- Chronic hepatitis.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis.
- Cholecystitis.
- Active cirrhosis.
- Metastatic tumors of the liver.
- Obstructive jaundice.
- Alcoholic cirrhosis.
- The mild increase is seen in :
- Myosotis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Shock.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Alcohol-acetaminophen syndrome.
- A significant increase in level has been in acute liver diseases.
- Moderately increase level is seen in chronic diseases of the liver and trauma to muscles.
- A mildly increased level is seen in myositis, Myocardial infarction, and infectious mononucleosis.
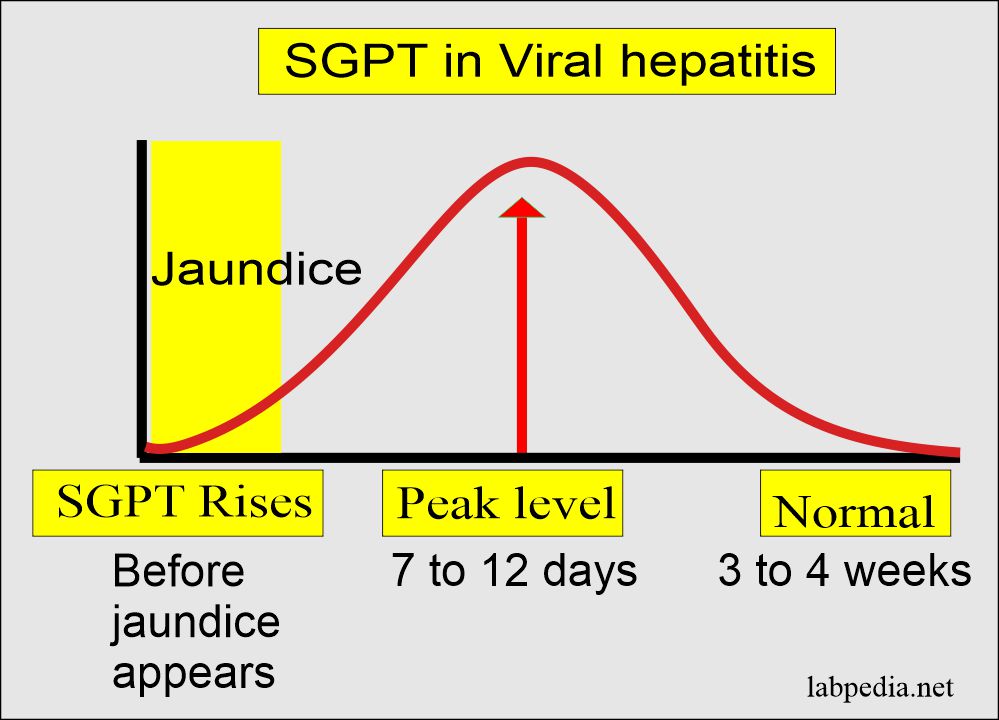
Acute Viral Hepatitis SGPT (ALT) Pattern:
- This rises before the appearance of jaundice.
- Peak level occurs between 7 to 12 days of jaundice.
- Then there is a gradual decrease in the level.
- Normal level after 3 to 4 weeks of the onset of jaundice.
- AST/ALT ratio, which is normally <1, becomes greater >1.
Table Showing The Increase Of SGPT In Various Conditions:
Clinical Condition | The Rise In SGPT Level With Reference To The Normal Value |
| Viral hepatitis and liver diseases | may reach 100 times |
| Infectious hepatitis | ALT > AST |
| Toxic hepatitis | Extremely high level |
| Infectious mononucleosis | 20 times |
| Intrahepatic cholestasis | maybe raised |
| Extrahepatic cholestasis | Very high level |
| Cirrhosis | 4 to 5 times or higher |
| Metastatic carcinoma | 5 to 10 times |
| Acute myocardial infarction | within normal limits or a very mild increase |
| Progressive muscular dystrophy | May reach 8 times |
| Dermatomyositis | May reach 8 times |
Comparison of AST/ALT
- AST (SGOT) is always is raised in acute myocardial infarction, where ALT (SGPT) will be normal unless there is damage to the liver.
- ALT (SGPT) is more raised in acute hepatobiliary obstruction than AST (SGOT).
- ALT (SGPT) is more specific than AST (SGOT) for liver cell injury.
- The AST/ALT ratio is higher in alcoholic liver diseases.
- AST (SGOT) is more sensitive to alcoholic liver cell injury.






0 Comments