Sample
- It is done on the serum of the patient and performs tests within one hour.
- How to get good serum: Take 3 to 5 ml of blood in the disposable syringe or a vacutainer. Keep the syringe for 15 to 30 minutes and then centrifuge for 2 to 4 minutes to get the clear serum.
- Serum should be separated immediately from the RBCs and stabilize the serum by adding disodium citrate monohydrate and adding 10 mg/ml of the serum.
- You can add acetic acid (5 mol/L) or 50 µL for 1 ml of the serum. This will lower the pH of the serum to 5.4, where the sample is stable.
- With all these precautions, the serum is stable at 37 °C (at room temperature) for several hours and one week if the serum is kept in the fridge.
- EDTA plasma is better because it stabilizes the acid phosphatase.
- A morning sample is preferred.
- Avoid hemolysis.
- The sample is stable for 24 hours at 2 to 8 °C.
- Try to do the test immediately.
- If serum is acidified below a pH of 6.5, that will stabilize the enzyme.
Precautions
- It has poor stability in whole blood.
- ACP is unstable at room temperature >37 °C.
- ACP is unstable if the pH is >7.0.
- The serum is separated immediately, and the test is performed within one hour.
- EDTA plasma is preferred that stabilizes the AP.
- Avoid prostatic massage in the last 48 hours.
- Rectal examination, prostatic massage, urinary catheterization, or instrumentation of the prostate in the previous 2 days before the test may give false high values.
- Hemolysis falsely raised the value and should be rejected.
- The lipemic serum also gives false value.
- 50% of activity lost if kept at room temperature.
- Drugs leading to elevated AP level are:
- Androgens in females.
- Clofibrate and antilipiodemic drugs.
- Specimen received >15 minutes later after the collection and hemolyzed sample give false values.
Purpose Of The Test (Indications):
- To diagnose the prostatic carcinoma by advising the estimation of Total acid phosphatase and the prostatic component.
- This test is more accurate in the diagnosis of advanced prostatic cancer than the early diagnosis.
- These two enzymes stage prostatic carcinoma and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
- The test for acid phosphatase can be done on a vaginal swab in rape cases because the seminal fluid is rich in acid phosphatase.
Pathophysiology:
- Acid phosphatase (AP) includes all phosphatases with optimal activity below a pH of 7.0. The prostatic AP has an optimum pH range of 5 to 6.
- AP is unstable, particularly at temperature >37 °C and pH level >7.0.
- The prostatic AP in serum is labile and may lose >50% of the AP in one hour at room temperature.
- If you do pacification of the serum to a pH <6.5, it will stabilize the enzymes.
- Source of AP:
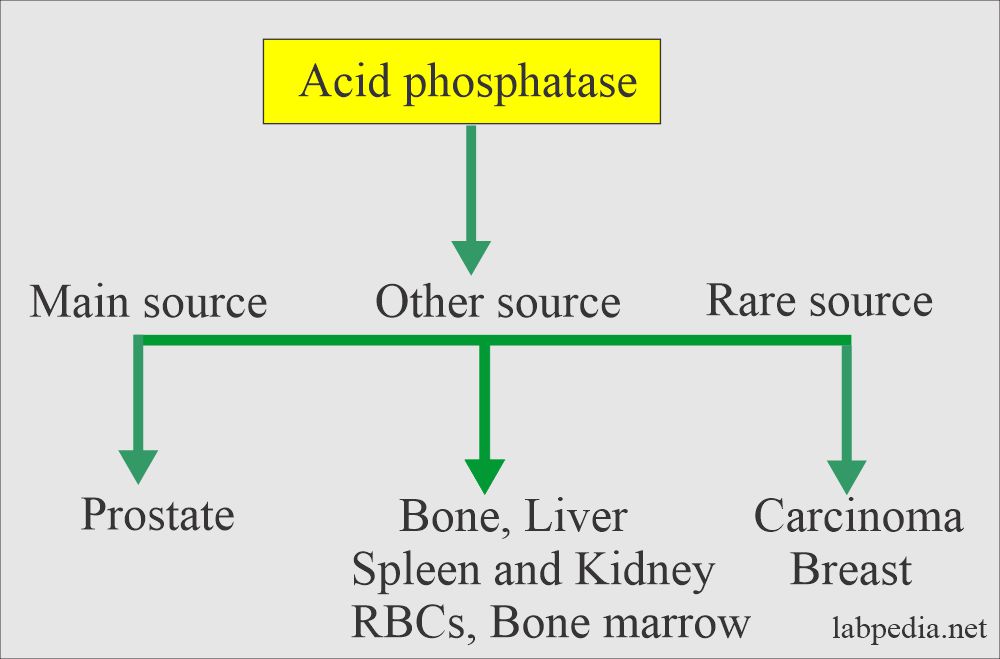
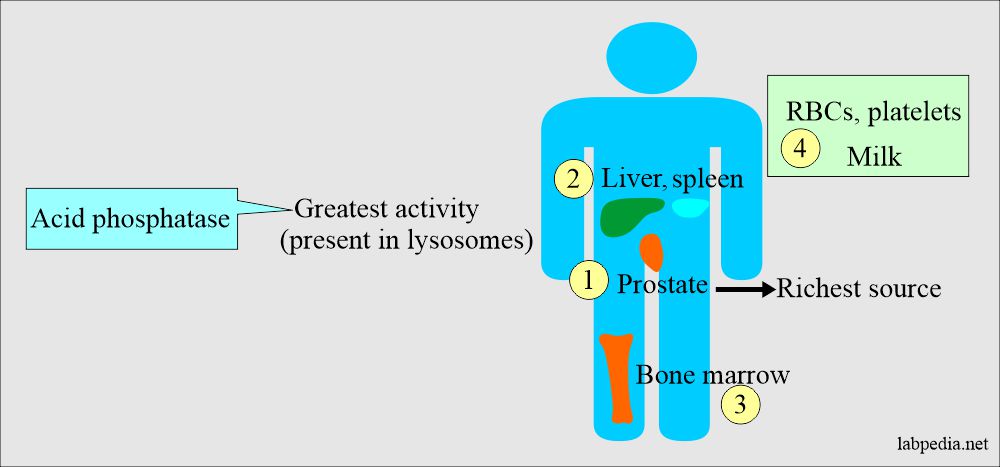
- Acid phosphatase enzymes are found in various tissue lysosomes like the Prostate, bone, kidney, platelets, semen, liver, and spleen, with the possible exception of RBCs.
- The prostate is the richest source. The majority of AP arises from the RBCs and prostatic tissue.
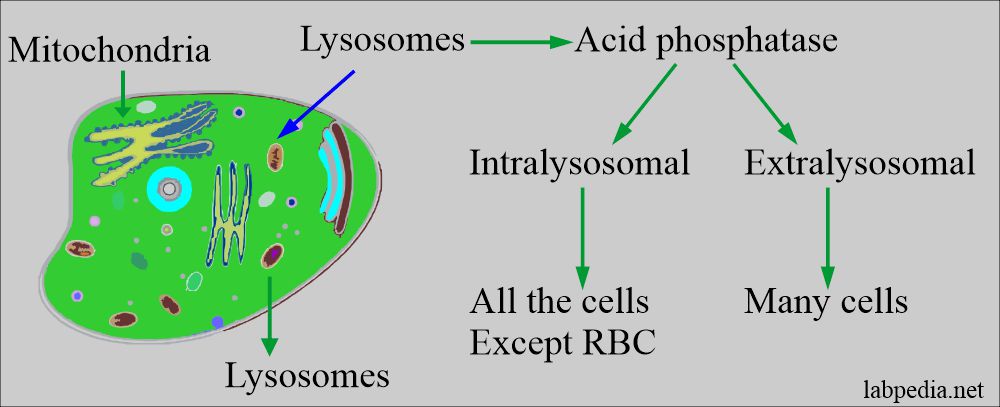
- Extralysosomal AP is also found in many cells.
- High levels are also found in white blood cells like monocytes and lymphocytes.
- Total acid phosphatase consists of a one-half prostatic component and the rest of the liver, disintegrating platelets, and RBCs.
- Acid phosphatase activity is 100 times more in the prostate than in other tissues, so the prostate is the richest source.
- Acid phosphatase (AP), derived from the prostate, has a pH optimum range of 5 to 6.
- All phosphatases have optimal activity below a pH of 7.0
- The difference in pH between acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase:
Acid phosphatase Alkaline phosphatase pH 5.0 >7.0
- As the prostatic component (PAP) is not raised in the early prostatic diseases, this is not a good screening enzyme.
- Acid phosphatase is a lysosomal enzyme, so the prostatic enzyme is found in the lysosome of prostatic epithelium and is a glycoprotein.
- Once prostatic cancer spreads, AP’s level starts rising and significantly raised when there is metastasis, particularly in the bone.
- The raised level in 80% of the patient with metastasis is age-related.
- It is raised in Prostatic carcinoma, particularly its prostatic component.
- Total AP is raised in Bone diseases.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase needs to be differentiated from the non-prostatic sources like RBCs source.
- Total AP = AP after tartarate inhibition = Prostatic AP.
- Some of the inhibitors discriminate between prostatic and nonprostatic AP.
- Prostatic AP is inhibited by the dextrorotatory tartrate ions when there is no action on the RBC isoenzyme AP.
- RBC AP is inhibited by the formaldehyde and cupric ions, where prostatic AP is resistant.
Normal
- Total acid phosphatase
- 2.5 to 3.7 ng /mL or 2.5 to 3.7 µg/L.
- or less than 3.0 mg /L.
- Prostatic acid phosphatase = <2.5 ng/mL (0 to 0.6 U/L).
- Another reference
- Adult 0.13 to 0.63 units/L at 37 °C
- or 2.2 to 10.5 units/L (SI units).
- Child 8.6 to 12.0 units/mL at 30 °C.
- Newborn 10.4 to 16.4 units /mL at 30 °C.
- Another source
- Prostatic AP = 0 to 0.6 U/L.
- RIA = 3 µg/L.
- Immunoassay = <20 µg/L.
Moderately Raised Levels Seen In, Other Than Prostatic Carcinoma:
- Niemann-Pick disease.
- Gaucher’s disease.
- Prostatitis and Benign prostatic hyperplasia ( BPH ).
- Urinary retention.
- Any cancer that has given metastasis to the bones.
- Myeloid Leukemia.
- Multiple myelomas.
- Paget disease.
- Sickle cell anemia.
- Renal diseases.
- Liver diseases like cirrhosis.
- Thrombocytosis.
- Hyperparathyroidism.
The Raised Level Is Seen In:
- Significantly raised level seen in prostatic carcinoma.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Prostatitis.
- Metastatic carcinoma of the prostate.
- Metastases to the bones.
The prostatic AP level is variable in the case of carcinoma prostate:
The AP values vary according to the methodology like RIA and immunoassay. The level of AP is related to the clinical staging of prostatic carcinoma.
- 5% to 10% of the prostatic carcinoma confined to the prostate has an elevated level of AP.
- 20% to 25% of the prostatic carcinoma shows elevated value with the extension of prostatic adenocarcinoma outside the prostatic capsules without distant metastasis.
- 75% to 80% of the cases show elevated AP with bone metastasis.
Important Facts:
- After the surgery, its level will drop in 3 to 4 days.
- With estrogen, therapy takes 3 to 4 weeks to drop the level.
- Acid phosphatase is not recommended for screening prostatic carcinoma because its level is not usually significantly raised until the tumor has metastasis.
- Acid phosphatase is not advised in routine to diagnose prostatic carcinoma, in case the following parameters are recommended:
- Per-rectal digital examination.
- Transurethral ultrasound image.
- Histologic examination of the prostatic biopsy.
- Total body scan.
- The Prostatic specific antigen is advised.
Medicolegal Importance:
- There is a high concentration in the semen, so its measurement is important in rape cases.
- Take the vaginal swab, keep it in 2.5% of broth, and store at 4 °C or room temperature.
- Result: In noncoital ladies, its value is 10 U/L and in the coital lady is >50 U/L.
- However, PSA is more specific and sensitive than acid phosphatase.
Test Value For The Layman:
- This test is advised for the diagnosis of prostatic cancer.
- It can be advised in case of rape on the vaginal swab.






0 Comments